Space Time
Space Time
Astronomers and cosmologists keep talking about spacetime. Einstein inserted it into his equations to describe his theories of relativity. It is a concept bantered around constantly by cosmologists.
What the heck is spacetime?
The current theory is that the universe was created at the time of the Big Bang when a tiny speck smaller than an atom popped into existence and expanded rapidly at faster than the speed of light. It turns out that spacetime, the very fabric of the universe, was created then and it was this spacetime that expanded. Inflation caused the tiny variations in the spacetime fabric to expand at different rates. This, in turn, caused the energy that filled spacetime to form matter that was clumped together and it was this clumping that allowed the first stars to form.

Spacetime is weird. If you have mass in spacetime it bends or curves the spacetime. This is what Einstein first proposed. He determined that the larger the mass in spacetime the more the gravity curves the spacetime. In other words, gravity is the result of mass curving spacetime. This is not what Newton proposed. He said that gravity was a force acting on mass. Einstein said that mass causes gravity force by curving space.
Cosmologists want to know how the universe we see formed such interesting and complex structures, such as galaxies, galaxy clusters and the filament structure of these clusters. It turns out the geometry of spacetime determines how matter and energy move through it. The original matter that formed in the early universe made spacetime curve to make matter in the form of hydrogen gas clump into stars. The original large stars went supernovae and the curvature of spacetime allowed the eventual formation of stars like our sun and the galaxies that these stars coalesced together.
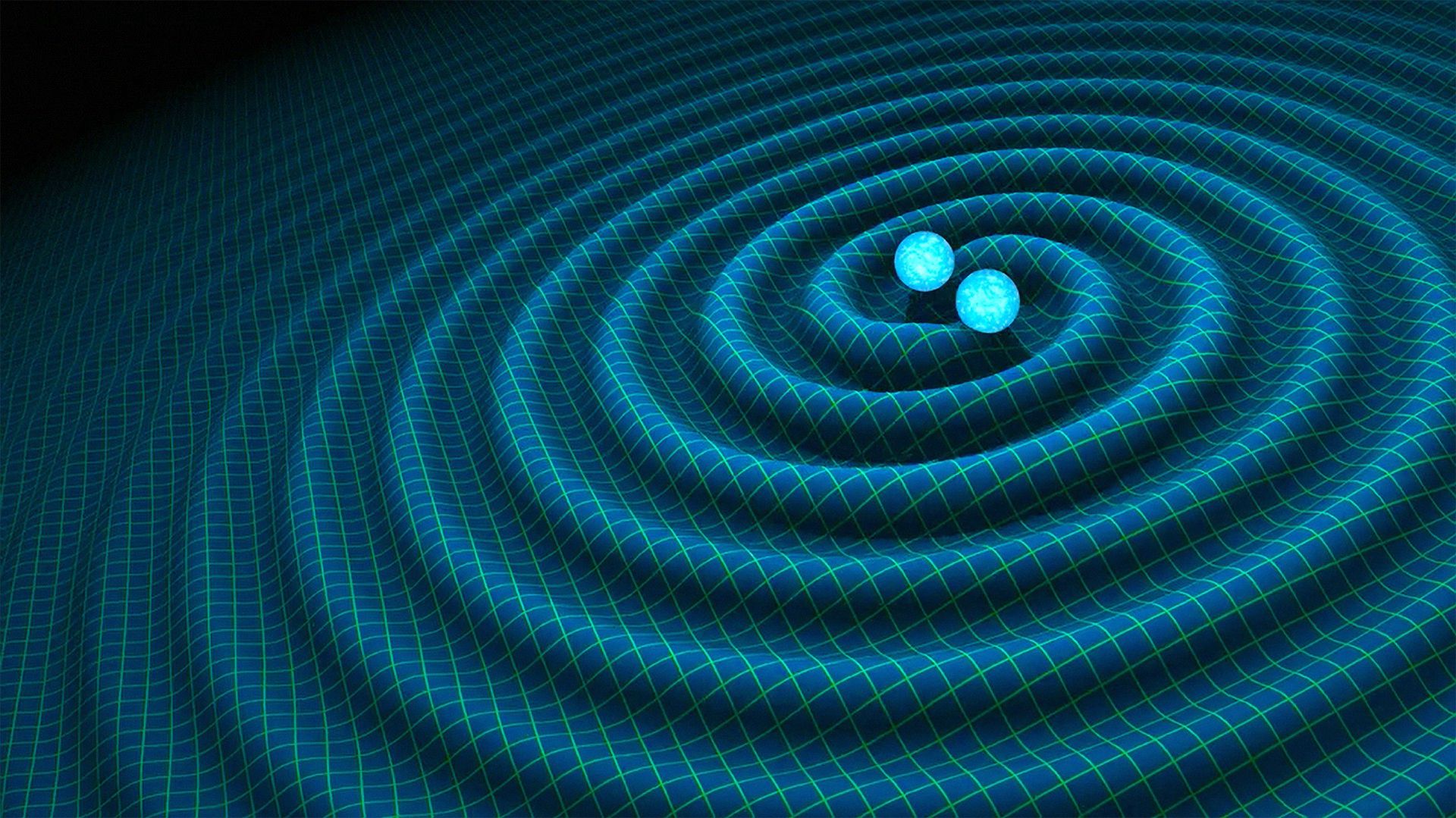
The evidence for the bending or curving of space was proven by the detection of gravitational waves from the collision of black holes and neutron stars. This shows that space is a fabric that can be bent and curved. In other words, space is not empty. It consists of energy and the fabric of spacetime. Gravitational waves are just like ripples in water from throwing a rock into the pond. They are like sound waves. In fact, these gravitational waves are in the audio frequency range.
Spacetime is intrinsically connected. Thus, time is not a constant, but rather depends upon the curvature of space. The one thing we do know is that the universe is full of spacetime and we see gravitational lensing that allows astronomers to see very distant red galaxies. The spacetime is actually curved by a galaxy cluster as if it were a lens to magnify much distant galaxies.
The time component of spacetime is also affected by curvature. Time has been ticking for 13.8 billion years. However, mass also can warp time. This means that time can speed up, slow down and even stop. This is what happens around a black hole. Time slows down near the event horizon and if something fell into the event horizon time would stop for that object. If one could create a spacecraft durable enough to survive being at the event horizon of a black hole, it would be possible to go into the future. Why is this? The reason is that time would slow down and even stop at the event horizon while the time away from the black hole would go on.
Earth's gravity affects time. If one goes up higher, there is a tiny change in the time, making time speed up slightly. This effect is insignificant but measurable using atomic clocks. This time correction is what's necessary for the satellites that provide us with accurate GPS.

Spacetime is actually expanding as the Universe expands, and this spacetime expansion is accelerating. This effect is called Dark Energy, but it really is the inception of negative energy into spacetime. It's believed that this effect is an energy component of space. If this is the case, the universe will become a cold lonely place in many trillions of years in which stars will burn out, leaving only black holes that will eventually evaporate.
No one knows the ultimate fate of the universe, but it's possible that the death of our universe will lead to the formation of a new universe. That gets into quantum physics. Quantum physicists believe that there is quantum spacetime and that means that our universe formed from the collapse of an old universe that crunches spacetime into a small spot that will then expand again. In other words, our universe could have gone through an infinite number of these expansion-contraction cycles.
One thing is for sure, and that is that spacetime rules our universe. We need to really understand this spacetime.
Thanks for reading.
Bạn đang đọc truyện trên: Truyen247.Pro