Plasma Stories
Plasma Stories
There are four states of matter; solid, liquid, gas and plasma. What makes the plasma state of matter so important is that it exists all over the universe in star atmospheres, nebulae and intergalactic space. It could be the most abundant form of matter in the universe.
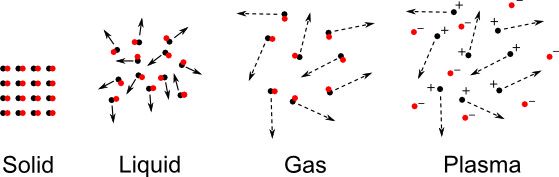
What exactly is plasma?
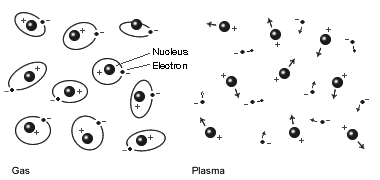
Most plasma exist as ionized gases. This is where the gas has its electrons stripped away, making it positively charged. Some plasma exists only partially ionized. What makes plasmas so interesting is that they are affected by electromagnetic fields. There are several ways to make plasma out of a gas, but the most important one is heat. One everyday use of plasma is in neon signs, but neon isn't the only gas that's used in signs and displays. Another natural plasma source is lightening. The electrical charge in a lightening bolt heats up air so that it becomes plasma.
Unlike gas, which is neutral, plasma is charged, but can also contain whole atoms that behave differently than normal because of being immersed in ionized gas.
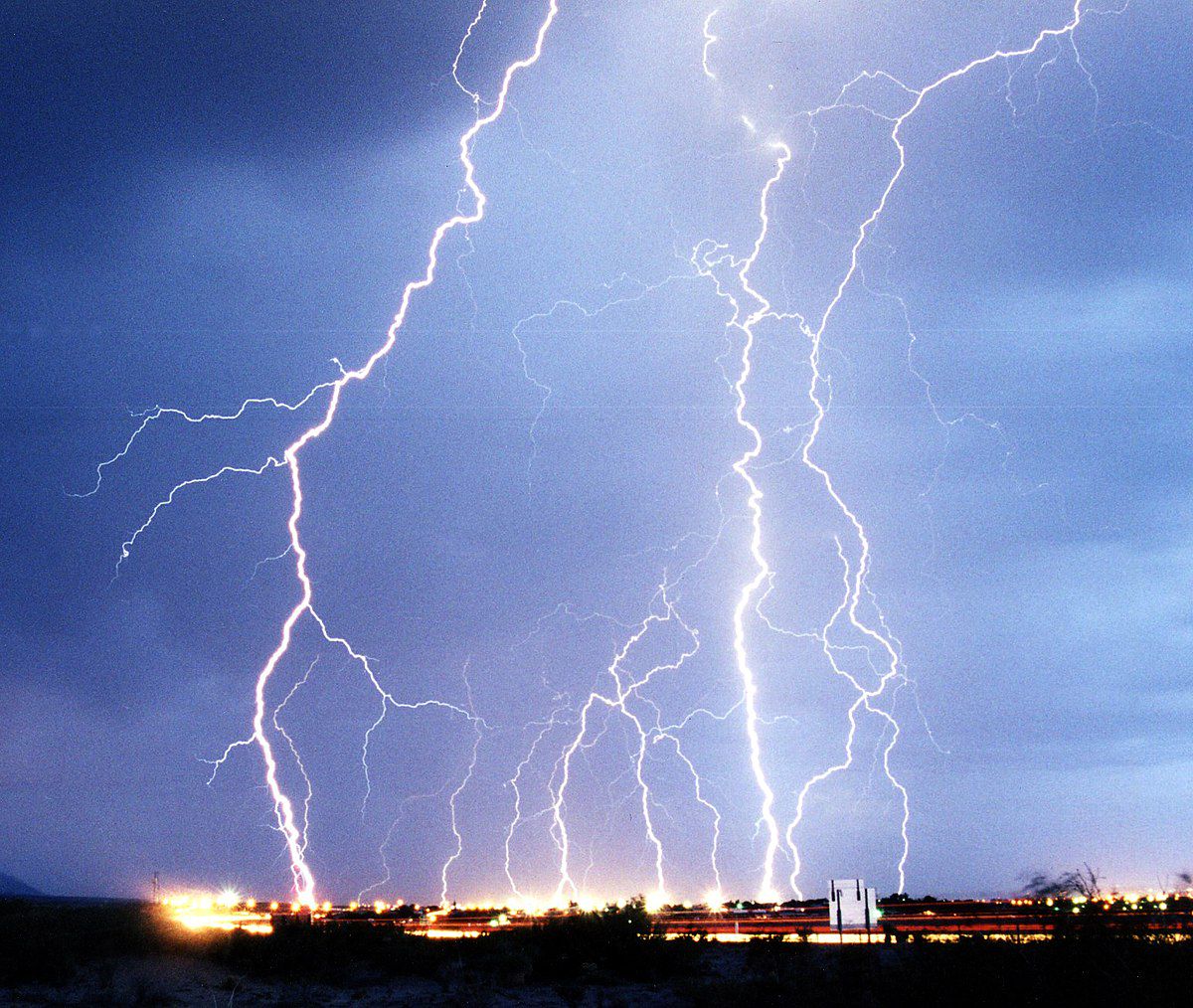

One thing to remember about plasmas is that they don't exist on Earth unless some force like lightening or extreme heat creates them. However, plasmas are very important for the creation of technology, including rocket propulsion, semiconductor production, fluorescent displays and spectroscopy.
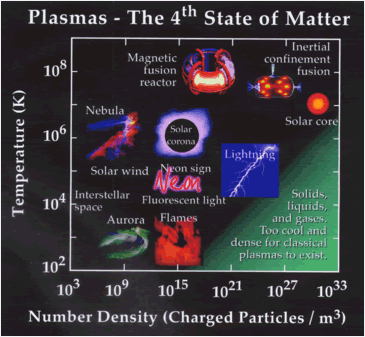
What I'm most interested in is the existence of plasmas in space.
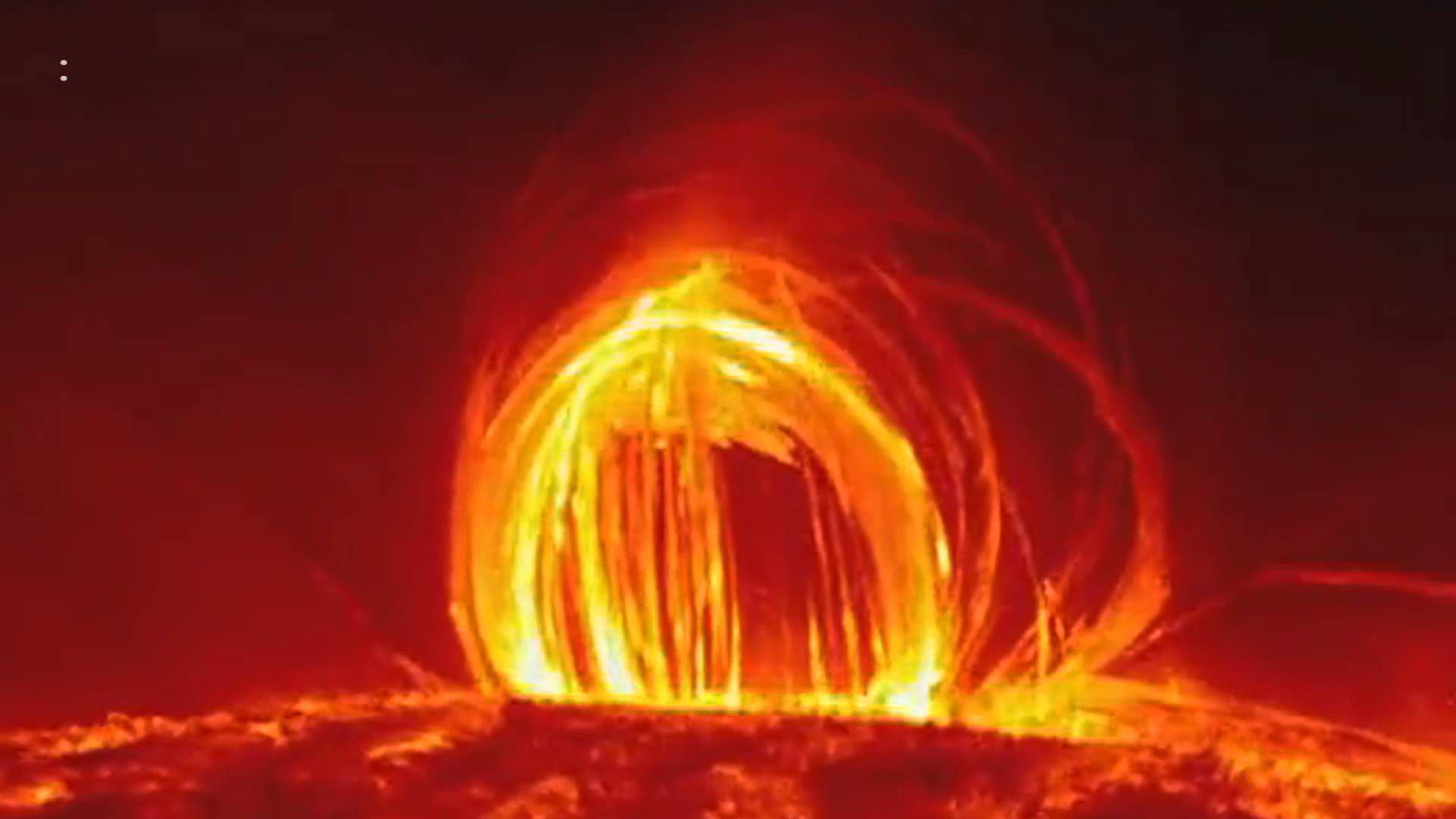

Number one on this list is the existence of plasmas after the Big Bang. This is what existed before recombination to make atoms of hydrogen. However, even after this period the universe has remained mostly plasma, especially in the intergalactic medium. Most of this space exists as rarefied plasma, mostly ionized hydrogen in the form of protons and electrons that are heated to 10 to 5 to 7th power Kelvin. Believe it or not, 10 to 5th power K is considered only warm by astrophysicists.

Nebulae are a good example of plasmas in space. These astronomical objects exist as ionized gas. The reason astronomers know this is because nearby stars emit radiation that excite these plasmas to make them visibly observable. The spectra of these excited gas clouds gives astronomers an understanding of their compositions. Nebulae also emit infrared, X-ray and radio waves. These types of plasmas can be recreated in the lab, and in the case of stars can be duplicated in fusion experiments.
The other property of plasma that astrophysicists are interested in is their interaction with magnetic fields, especially in stars like our sun. Our sun's atmosphere is plasma tortured by strong magnetic lines that twist, turn and collide in spectacular displays of energy called flares and coronal mass ejections.

Tesla was also fascinated by plasma, and he demonstrated his ability to create spectacular displays of electromagnetic interaction with plasmas.
Another important use for the fourth state of matter is to create a very hot ball of plasma that can be isolated from its surroundings by a magnetic field. This is the premise of creating fusion reactions on Earth. However, millions of degrees of heat is needed to initiate fusion. Currently, this is not an efficient process, but it will be in the future.
Thanks for reading.
Bạn đang đọc truyện trên: Truyen247.Pro