Dating Things
Dating Things
We've all seen these reports in the news about the age of artifacts that had been found by archeologists, historians, museum curators, criminologists, and paleontologists. Just how do they date ancient or even current objects?
This is a fascinating subject because it shows how the science of dating things has evolved over the ages.
Criminal investigators are called upon to identify the time of death of a murder victim. In the past, this was mostly a guessing game. Criminal investigators knew how long it took for rigor mortis to set in or how long for the body temperature to drop, but even these variables were not reliable if the body lay outside. It turns out that the best way a body found outdoors time of death can be determined is by the kind and quantity of insect infestations (development stages of larvae for example), such as from a blowfly. People have donated their bodies after death for these kinds of studies. I realize that this sounds gross but it works. There are dead body gardens where bodies are stored to determine these insect effects.

Artistic objects that are not much more than 50,000 years old can be dated using carbon dating or radiocarbon dating. Carbon 14 has a half-life of approximately 5730 years. While a tree or a bone is alive, the carbon 12 to carbon 14 ratio is that of the natural environment in the air. Carbon 14 is created by bombardment of nitrogen-14 with gamma rays in the stratosphere and upper troposphere. The resultant Carbon 14 reacts with oxygen to make radioactive carbon dioxide. This CO2 with Carbon 14 is absorbed by plants in photosynthesis and by animals that eat the plants. The ratio of Carbon 14 to Carbon 12 is only 1.5 parts per 10 to the 12th power. That's not very much, but it's good enough to obtain a Carbon 14 decay rate after the plant or animal part is no longer alive.
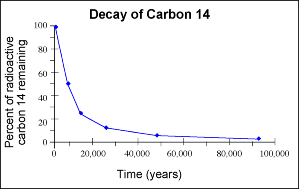
The sample is either oxidized and the gaseous carbon dioxide is measured for radioactivity or it's measured directly for radioactivity by dissolving it in a solvent at low temperature that gives off UV when a radioactive carbon14 atom decays and emits a beta particle, essentially a high-energy electron (scintillation). This is what they call beta counting. Scintillation counters detect the number of counts of radioactivity per gram per unit of time. One way to improve the result is to use enhancement by using a thermal diffusion column. This process takes a month but makes the sample appear to be 10 times as large.
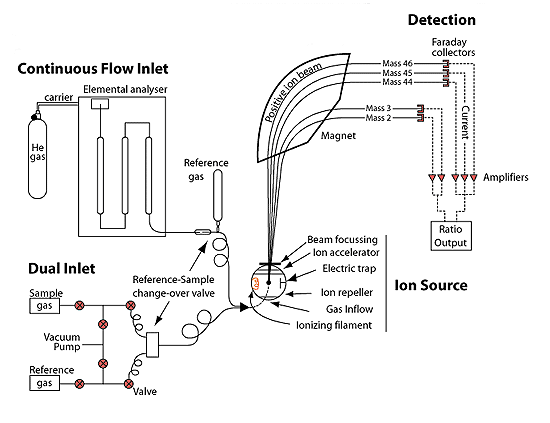
Those methods have been supplanted with more sophisticated procedures, but the end result is to determine the amount of radioactivity in a given sample. Although there are lots of considerations as to purity and accuracy, this method is reliable. However, there are difficulties when the sample is not representative of the object being measured, as was the case with attempts to date the Shroud of Turin. Contamination is definitely a problem.
Historians tend to use more subtle means to date an artistic object. They often are aware of the materials that a specific culture used to create art (such as the type of paint or kind of materials used to paint on) or they can identify the artist and know when they were alive. There is no exact method. Some historians use carbon dating. Others can date wooden objects by counting the tree ring growth separations.
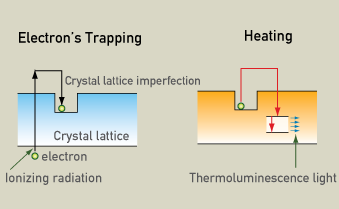
Pottery can be dated roughly using thermo luminescence, which gives the age since clay firing. This has to do with measuring a weak radiation dose that is indicative of the age of crystalline material. This radiation accumulates with time after the object is fused or removed from its natural environment. Apparently, electron traps are created with time in imperfections in the crystalline structure of the fused clay by absorption of natural radiation. With time this radiation effect builds up and can be measured. Both alpha and beta particles can be used to determine the accumulated radiation of a sample. Gamma radiation is also used depending on the type of sample.

Radiometric methods can be used to date rocks. Potassium-argon dating and Uranium-lead dating are two of the most used procedures. Potassium 40 has a half-life of 1.248 times 10 to the 9th power years. Potassium 40 decays to Argon 40. Measuring the amount of Argon 40, a radioactive isotope, gives one an idea of how long the rock has solidified from molten magna. Using this method gives scientists one method of dating the rocks found in a specific layer of earth.
Uranium 238 decays to Lead 206 and Uranium 235 decays to Lead 207. By use of this method, one can determine the age of rocks back to from 1 million to 4.5 million years with a 0.1 to 1 percent accuracy.
As you can see there are methods to date things, and this idea is important to an understanding of history and geological processes. They have allowed scientists to determine how old the Earth is and how old artifacts and objects are relative to human history.
Thanks for reading.
Bạn đang đọc truyện trên: Truyen247.Pro