AGP L-1
Let's start with Advanced General Psychology. Psychology-The scientific study of behavior and mental processes and how they are affected by an organism's physical, state, mental state, and external environment
There are 7 Major Schools of Thought in Psychology:
1.Structuralism
2.Functionalism
3.Gestalt Psychology
4.Behaviorism
5.Psychoanalysis
6.Humanistic Psychology
7.Cognitive Psychology
Before we get into this individual thoughts, lets see what is consciousness since it is the basic block of all.
Consciousness: Consciousness refers to your individual awareness of your unique thoughts, memories, feelings, sensations, and environment.

Your conscious experiences are constantly shifting and changing. For example, in one moment you may be focused on reading this article. Your consciousness may then shift to the memory of a conversation you had earlier with a friend. Next, you might notice how uncomfortable your chair is, or maybe you are mentally planning dinner. This ever-shifting stream of thoughts can change dramatically from one moment to the next.
One of the problems with the study of consciousness is a lack of a universally accepted operational definition. Today, consciousness is often viewed as an individual's awareness of their own internal states as well as the events going on around them. If you can describe something you are experiencing in words, then it is part of your consciousness.
In psychology, consciousness is occasionally confused with the conscience. It is important to note that while consciousness involves awareness of yourself and the world, your conscience is related to your morality and sense of right or wrong.
structuralism
Structuralism can be defined as the study of the elements of consciousness. The focus of structuralism was on reducing mental processes down into their most basic elements. In order to reduce a normal conscious experience into basic elements, structuralism relied on a method called introspection. Major thinkers associated with structuralism include Wilhelm Wundt and Edward Titchener
Introspection - Individual will be tested for different stimuli (senses) and their response will be recorded .

Functionalism
It was strongly influenced by Darwin's theory of natural selection; focused on functions of consciousness rather than on its structure.
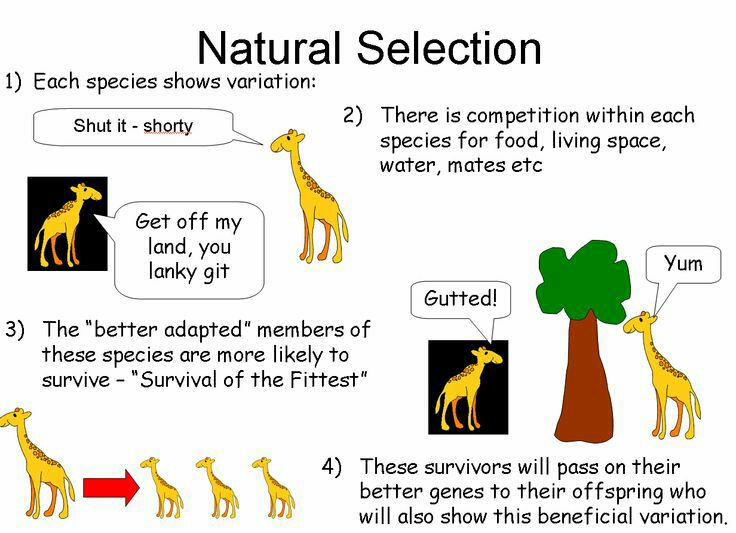

Gestalt Psychology
Gestalt psychology is a school of psychology based upon the idea that we experience things as unified wholes. This approach to psychology began in Germany and Austria during the late 19th century in response to the molecular approach of structuralism. Instead of breaking down thoughts and behavior to their smallest elements, the gestalt psychologists believed that you must look at the whole of experience. According to the Gestalt thinkers, the whole is greater than the sum of its parts.
Behaviorism
Behaviorism became a dominant school of thought during the 1950s. It was based upon the work of thinkers such as:
John B. Watson
Ivan Pavlov
B. F. Skinner
Behaviorism suggests that all behavior can be explained by environmental causes rather than by internal forces. Behaviorism is focused on observable behavior. Theories of learning including classical conditioning and operant conditioning were the focus of a great deal of research.
The behavioral school of psychology had a significant influence on the course of psychology, and many of the ideas and techniques that emerged from this school of thought are still widely used today.
Behavioral training, token economies, aversion therapy and other techniques are frequently used in psychotherapy and behavior modification programs.
Psychoanalysis
Psychoanalysis is a school of psychology founded by Sigmund Freud. This school of thought emphasized the influence of the unconscious mind on behavior.
Freud believed that the human mind was composed of three elements: the id, the ego, and the superego. The id consists of primal urges while the ego is the component of personality charged with dealing with reality. The superego is the part of personality that holds all of the ideals and values we internalize from our parents and culture.
Freud believed that the interaction of these three elements was what led to all of the complex human behaviors.
Other major psychoanalytic thinkers include:
Anna Freud
Carl Jung
Erik Erikson
Humanistic Psychology
Humanistic psychology developed as a response to psychoanalysis and behaviorism. Humanistic psychology instead focused on individual free will, personal growth and the concept of self-actualization. While early schools of thought were primarily centered on abnormal human behavior, humanistic psychology differed considerably in its emphasis on helping people achieve and fulfill their potential.
Major humanist thinkers include:
Abraham Maslow
Carl Rogers
Humanistic psychology remains quite popular today and has had a significant influence on other areas of psychology including positive psychology. This particular branch of psychology is centered on helping people living happier, more fulfilling lives.
Cognitive Psychology
Cognitive psychology is the school of psychology that studies mental processes including how people think, perceive, remember and learn. As part of the larger field of cognitive science, this branch of psychology is related to other disciplines including neuroscience, philosophy, and linguistics.
Cognitive psychology began to emerge during the 1950s, partly as a response to behaviorism. Critics of behaviorism noted that it failed to account for how internal processes impacted behavior. This period is sometimes referred to as the "cognitive revolution" as a wealth of research on topics such as information processing, language, memory, and perception began to emerge.
One of the most influential theories of this school of thought was the stages of cognitive development theory proposed by Jean Piaget
Bạn đang đọc truyện trên: Truyen247.Pro